systemd overview
Systemd သည် rhel 7 မှာ အသစ် အသုံးပြုလာသော new init system ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ ယခင် အသုံးပြုခဲ့သော SysVinit init system နေရာမှာ အစားထိုးအသုံးပြုခြင်းဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ အရင် init system တွေလိုပဲ run level management, system services and daemons တွေကို manage လုပ်ပေးတာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Systemd ရဲ့အားသာချက် ကတော့ SysVinit ထက်စာရင် လုပ်ဆောင်ချက်ပိုမိုမြန်ဆန်ပြီး system startup scripts တွေမှာ parallel processing ပုံစံမျိုးနောက် system state ကို snapshot သတ်မှတ် နိုင်တာမျိုး တွေဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ နောက် device mounting control, system logging features (journalctl mode) စတာတွေဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
#systemctl command
systemctl command သည် systemd နှင့် အဓိက interacting လုပ်ရသည့် primary command ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ systemctl command ကိုအသုံးပြုပြီးတော့ services တွေကို start/stop လုပ်နိုင်တယ် နောက် enable/disable, status စတာတွေ နောက်ပြီးတော့ အရင်တုန်းက runlevel တွေ သတ်မှတ်နိုင်သလို အခု systemctl command ဖြင့်လဲ သတ်မှတ်နိုင်ပါတယ်။ အရင်တုန်းက SysVinit မှာ သုံးခဲ့တဲ့ အခေါ်အဝေါ် မဟုတ်တော့ဘဲ graphical mode, multiuser mode, rescue mode, emergency mode ပုံစံမျိုးသုံးပါတယ်။
#systemctl and systemd units
rhel 7 မှာ အသုံးပြုတဲ့ systemd မှာ unit types အမျိုးမျိုးရှိပါတယ်။ #systemctl command ဖြင့် ထို units type တွေကို manage လုပ်နိုင်ပါတယ်။
#systemctl -t help command ဖြင့် available units type တွေကို ကြည့်နိုင်ပါတယ်။ အခု tutorial မှာ service unit နဲ့ target unit (boot target) အကြောင်းကို ပြောမှာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Systemd သည် rhel 7 မှာ အသစ် အသုံးပြုလာသော new init system ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ ယခင် အသုံးပြုခဲ့သော SysVinit init system နေရာမှာ အစားထိုးအသုံးပြုခြင်းဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ အရင် init system တွေလိုပဲ run level management, system services and daemons တွေကို manage လုပ်ပေးတာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Systemd ရဲ့အားသာချက် ကတော့ SysVinit ထက်စာရင် လုပ်ဆောင်ချက်ပိုမိုမြန်ဆန်ပြီး system startup scripts တွေမှာ parallel processing ပုံစံမျိုးနောက် system state ကို snapshot သတ်မှတ် နိုင်တာမျိုး တွေဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ နောက် device mounting control, system logging features (journalctl mode) စတာတွေဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
#systemctl command
systemctl command သည် systemd နှင့် အဓိက interacting လုပ်ရသည့် primary command ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ systemctl command ကိုအသုံးပြုပြီးတော့ services တွေကို start/stop လုပ်နိုင်တယ် နောက် enable/disable, status စတာတွေ နောက်ပြီးတော့ အရင်တုန်းက runlevel တွေ သတ်မှတ်နိုင်သလို အခု systemctl command ဖြင့်လဲ သတ်မှတ်နိုင်ပါတယ်။ အရင်တုန်းက SysVinit မှာ သုံးခဲ့တဲ့ အခေါ်အဝေါ် မဟုတ်တော့ဘဲ graphical mode, multiuser mode, rescue mode, emergency mode ပုံစံမျိုးသုံးပါတယ်။
#systemctl and systemd units
rhel 7 မှာ အသုံးပြုတဲ့ systemd မှာ unit types အမျိုးမျိုးရှိပါတယ်။ #systemctl command ဖြင့် ထို units type တွေကို manage လုပ်နိုင်ပါတယ်။
#systemctl -t help command ဖြင့် available units type တွေကို ကြည့်နိုင်ပါတယ်။ အခု tutorial မှာ service unit နဲ့ target unit (boot target) အကြောင်းကို ပြောမှာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Use #systemctl {start,stop,restart} and {enable, disable} services in rhel7
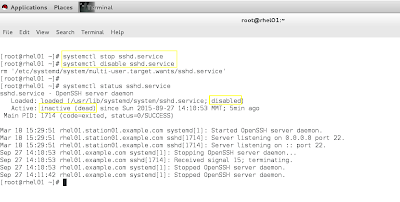
rhel 6 မှာ services တွေကို start, stop လုပ်မယ်ဆိုလျှင် #service sshd {start,stop,status} နှင့် အသုံးပြုပြီး အခု rhel 7 မှာ ဆိုလျှင် #systemctl {start,stop,status} sshd.service ပုံစံမျိုးဖြင့်အသုံးပြုပါတယ်။ #chkconfig command ကို အရင် rhel 6 မှာ services enable and disable အတွက် အသုံးပြုခဲ့ပြီး အခု rhel 7 တွင် #systemctl enable | disable service name ပုံစံဖြင့်အသုံးပြုပါတယ်။ services restart အတွက် #systemctl restart sshd.service ဆိုပြီ: အသုံးပြုပါတယ်။
#systemctl is-{enable,active} and masking features
နောက်ထပ် rhel 7 မှာ အသစ်ပါ၀င်လာတဲ့ new usages တွေ အနေနဲ့ #systemctl is-enable, #systemctl is-active ဆိုသည်မှာ service တစ်ခု ကို enable (or) disable ဖြစ်နေလားဆိုတာကို long format status command ဖြင့် မကြည့်ပဲ short format ဖြင့် ကြည့်ချင်လျှင် အသုံးပြုပါတယ်။
နောက်ထပ် new usage အသစ်ဖြစ်တဲ့ #systemct mask command ၏ အလုပ်လုပ်ပုံမှာ system ထဲမှာ conflict ဖြစ်နိုင်တဲ့ services တွေ ရှိနိုင်ပါတယ် ဥပမာ system ၏ firewall ကို manage လုပ်တဲ့အခါ အသုံးပြုတဲ့ iptables service နှင့် အခု rhel 7 မှာ iptables ကို replace လုပ်လိုက်တဲ့ firewalld service တို့က နှစ်ခုစလုံး running ဖြစ်နေလို့မရပါဘူး #systemctl stop ဖြင့် ပိတ်လို့ ရပေမယ့် mask ကို အသုံးပြုထားလျှင် ထို service ကို မှားပြီး start လုပ်မိရင်တောင် masking လုပ်ထားသည့် အတွက် service start ဖြစ်မှာ မဟုတ်ပါ။ mask လုပ်ထားသည့် service ကို ပြန်#unmask လုပ်မှသာ ပြန်လည် အသုံးပြုနိုင်မှာဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ တစ်နည်းအားဖြင့် system crash ဖြစ်စေမယ့် services တွေကို ensure ဖြစ်အောင် stop services ထက်စာရင် mask ဖြင့် အသုံးပြုတာ ပိုမိုကောင်းမွန်ပါတယ်။
Managing Boot Target with #systemctl
system ၏ default boot target ကို manage လုပ်တာဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ rhel 6 မှာ ဆိုလျှင် run level 1,2,3 etc စသည်ဖြင့် သတ်မှတ်သလို ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ rhel 7 မှာ boot target 4 မျိုး ရှိပါတယ်။
- graphical.target (support system with graphical-mode)
- multiuser.target (support system with termial console mode)
- rescue.target (support system with basic system mode)
- emergency.target (support system with read-only mode)
system စတက်ကတည်းက default အနေနဲ့ multiuser.target ဖြင့် တက်စေချင် လျှင် #systemctl set-default command ဖြင့် အသုံးပြုရပါမယ်။
emergency mode နှင့် rescue mode ကိုတော့ system maintenance လုပ်ရာမှာ အသုံးပြုပါတယ်။ #systemctl command ဖြင့် အသုံးပြုနိုင်သလိုအသုံးပြုနိုင်သလို grub boot menu (linux 16 last line) ထဲမှာ edit လုပ်ပြီး systemd.unit=rescue.target အနေနဲ့ အသုံးပြုနိုင်ပါတယ်။
Enjoy Reading and Thank You!!!
Enjoy Reading and Thank You!!!
Please also Like and Follow Root Of Info Page








ေနာက္ထပ္ tutorial ေတြေမ်ွာ္ေနပါတယ္ အကို
ReplyDeleteအရမ္းအေထာက္အကူျဖစ္ပါတယ္။ ဆက္လက္မွ်ေ၀ေပးပါခင္ဗ်ာ